Geometry settings¶
The geometry iterator has a variety of settings which can impact its output.
All settings can be accessed with C++ and Python, but only some are exposed in IfcConvert via command line arguments.
Here’s an example of changing settings in C++:
SerializerSettings settings;
settings.set(IfcGeom::IteratorSettings::APPLY_DEFAULT_MATERIALS, true);
Here’s an example of changing settings in Python:
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
settings.set("apply-default-materials", True)
Iterator instance settings¶
These settings are specific to an individual instance of an iterator object.
exclude¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
LIST OF OBJ |
|
NULL |
By default, all possible geometry in the IFC model is processed. If an exclude filter is specified, those geometries are excluded. Note that the include and exclude options are mutually exclusive.
See include for more details.
include¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
LIST OF OBJ |
|
NULL |
By default, all possible geometry in the IFC model is processed. If an include filter is specified, only geometry from the included elements are processed.
In IfcConvert, this is specified using the following syntaxes:
IfcConvert model.ifc out.glb --include=entities IfcWall
IfcConvert model.ifc out.glb --include=layers A-WALL
IfcConvert model.ifc out.glb --include=attribute GlobalId 1VQ5n5$RrEbPk8le4ZCI81
IfcConvert model.ifc out.glb --include=attribute Name Foo
IfcConvert model.ifc out.glb --include=attribute Description Bar
IfcConvert model.ifc out.glb --include=attribute Tag 123456
IfcConvert also allows using --include+ which includes all products
decomposed by that filter. For example, the following filter will process any
element with the attribute Name of Level 1, as well as all child elements. Child
elements include IsDecomposedBy, HasOpenings, FillsVoid, and
ContainedInStructure.
IfcConvert model.ifc out.glb --include+=attribute Name "Level 1"
In C++, this is set when the iterator is constructed:
IfcGeom::Iterator geom_iterator(settings, ifc_file, filter_funcs, num_threads);
In Python, this is set when the iterator is constructed, and requires a list of IFC entity instances:
iterator = ifcopenshell.geom.iterator(settings, ifc_file, include=ifc_file.by_type("IfcWall"), exclude=None)
num_threads¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
INT |
|
1 |
Number of parallel processing threads for geometry interpretation.
In C++, this is set when the iterator is constructed:
IfcGeom::Iterator geom_iterator(settings, ifc_file, filter_funcs, num_threads);
In Python, this is set when the iterator is constructed:
import multiprocessing
iterator = ifcopenshell.geom.iterator(settings, ifc_file, num_threads=multiprocessing.cpu_count())
Iterator settings¶
These settings are set within the iterator settings object and can be shared between iterator instances.
angle_unit¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
DOUBLE |
|
1 |
Override the plane angle unit being defined in the IFC.
apply-default-materials¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
True |
Given the command invocation:
IfcConvert model.ifc d.dae -yv --include attribute GlobalId 3bXiCStxP6Fgxdej$yc50U
You will find log messages along the lines of
[Warning] {3bXiCStxP6Fgxdej$yc50U} No material and surface styles for: #333=IfcCovering(‘3bXiCStxP6Fgxdej$yc50U’,#1,’Compound Ceiling:Gypsum Board:187483’,$,’Compound Ceiling:Gypsum Board’,#17840,#17052,’187483’,.CEILING.)
This means that there is no IfcStyledItem associated to the representation items and that the element does not have an IfcMaterial association with IfcMaterialRepresentation from which we can derive a style (colour) for the element.
The interactive session below shows how with this setting enabled you will get a default generated material from the IFC element entity type and material indices of 0 pointing to that. With this setting disabled the material index would be -1 to indicate a missing style. Note that there is one material index for every triangle in the list of shp.geometry.faces.
>>> import ifcopenshell, ifcopenshell.geom
>>> f = ifcopenshell.open("model.ifc")
>>> s = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
>>> # By default setting is enabled, we disable it for demonstration.
>>> s.set("apply-default-materials", False)
>>> c = f["3bXiCStxP6Fgxdej$yc50U"]
>>>
>>> shp = ifcopenshell.geom.create_shape(s, c)
>>> shp.geometry.material_ids
(-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1)
>>> [(m.name, m.diffuse) for m in shp.geometry.materials]
[]
>>>
>>> s.set("apply-default-materials", True)
>>> shp = ifcopenshell.geom.create_shape(s, c)
>>> shp.geometry.material_ids
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
>>> [(m.name, m.diffuse) for m in shp.geometry.materials]
[('IfcCovering', colour 0.7 0.7 0.7)]
This is enabled by default for the IfcConvert serializers as they will not gracefully handle -1 material indices and allows users to quickly assign colours based on entity types in their modelling applications.
boolean-attempt-2d¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
True |
Try to perform boolean subtractions in 2d. This can result in 2-3x faster geometry processing.
building-local-placement¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
In the typical IfcSite > IfcBuilding > IfcBuildingStorey > … hierarchy of elements, don’t incorporate the ObjectPlacement of the IfcBuilding and above in the placement of elements in the output. This is useful when there is a large offset in this placement that reduces precision in further processing.
circle-segments¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
INT |
|
16 |
Number of segments to approximate full circles in CGAL kernel.
context-identifiers¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
LIST OF STRING |
N/A |
NULL |
By default, geometry is processed from all geometric representation contexts.
In C++ and Python, it is possible to specify exactly which contexts should be
processed, by passing in a list of strings, where the strings are the
ContextIdentifier attribute of the contexts. Typically used to target only
Body representations or non-Body representations.
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
settings.set("context-identifiers", ["Body", "Axis"])
context-ids¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
LIST OF INT |
N/A |
NULL |
By default, geometry is processed from all geometric representation contexts. In C++ and Python, it is possible to specify exactly which contexts should be processed, by passing in a list of integers, where the integers are the IDs of the contexts. Typically used to target only Body representations or non-Body representations.
Here is an example in C++:
SerializerSettings settings;
std::vector<int> context_ids;
// ...
settings.set_context_ids(context_ids);
Here is an example in Python:
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
contexts = [c.id() for c in ifc_file.by_type("IfcGeometricRepresentationContext") if c.ContextIdentifier == "Body"]
settings.set("context-ids", contexts)
context-types¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
LIST OF STRING |
N/A |
NULL |
By default, geometry is processed from all geometric representation contexts.
In C++ and Python, it is possible to specify exactly which contexts should be
processed, by passing in a list of strings, where the strings are the
ContextType attribute of the contexts. Typically used to target only Body
representations or non-Body representations.
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
settings.set("context-types", ["Plan"])
convert-back-units¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Internally IfcOpenShell uses meters as the global length unit to do calculations. This setting restores the coordinate positions after conversion by multiplying the factor of the IfcUnit with UnitType=LENGTHUNIT into the output geometry coordinate values.
debug¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Write boolean operands to file in current directory for debugging purposes.
dimensionality¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
1 |
By default, IfcOpenShell only processes surface and solid geometry. You can change this to include edge and wire geometries in the geometric output.
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
settings.set("dimensionality", ifcopenshell.ifcopenshell_wrapper.CURVES) # 0
settings.set("dimensionality", ifcopenshell.ifcopenshell_wrapper.SURFACES_AND_SOLIDS) # 1, default
settings.set("dimensionality", ifcopenshell.ifcopenshell_wrapper.CURVES_SURFACES_AND_SOLIDS) # 2
disable-boolean-result¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Disables the evaluation of IfcBooleanResult and simply returns FirstOperand.
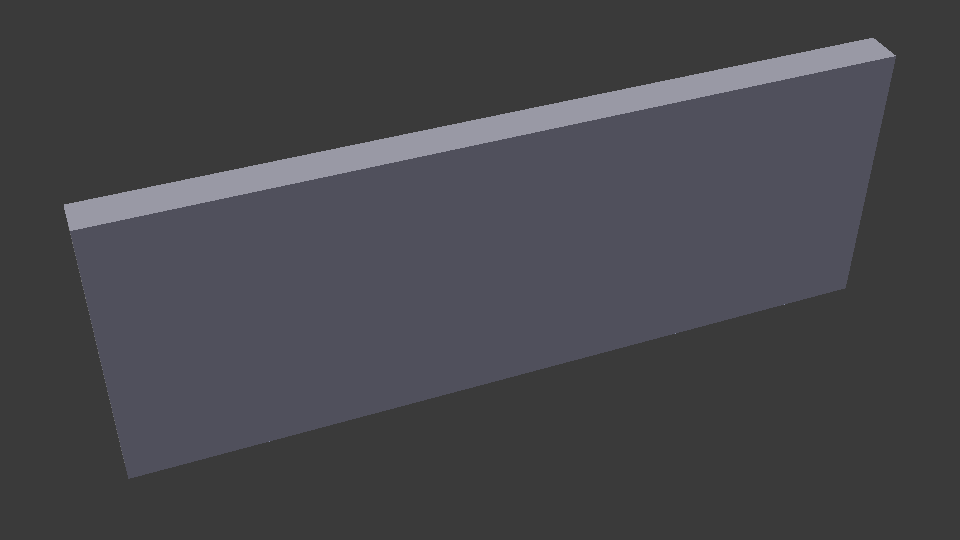
disable-opening-subtractions¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
As in most viewer applications, IfcOpeningElement geometry is subtracted from their host elements. This setting disables this behavior.
IfcConvert model.ifc d1.dae -yv --include attribute GlobalId 2O2Fr$t4X7Zf8NOew3FNr2
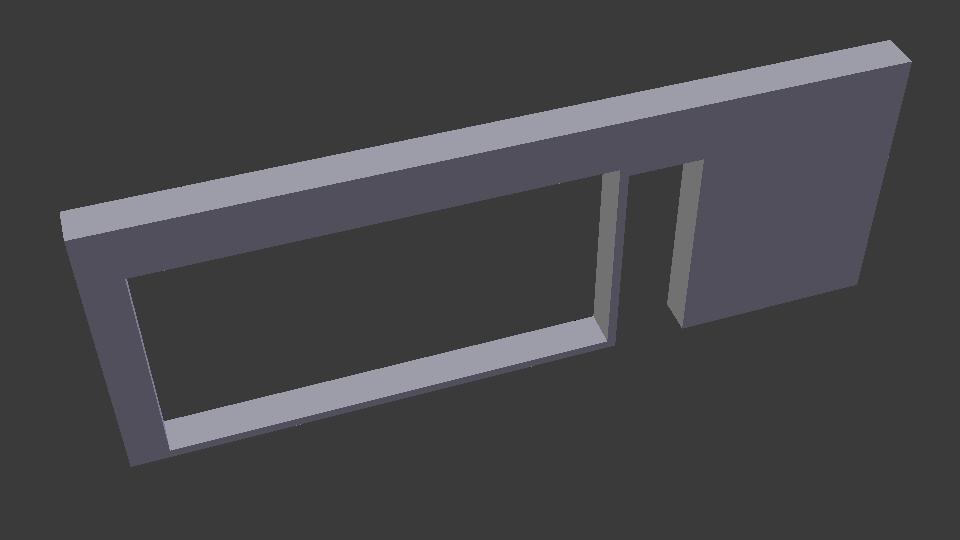
IfcConvert model.ifc d3.dae --disable-opening-subtractions -yv --include attribute GlobalId 2O2Fr$t4X7Zf8NOew3FNr2
Note
Disabling this settings will reduce processing time and improve robustness as it involves 3D Boolean operations.
For example, if you want to set this setting in a python script you can use the following:
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
settings.set("disable-opening-subtractions", True)
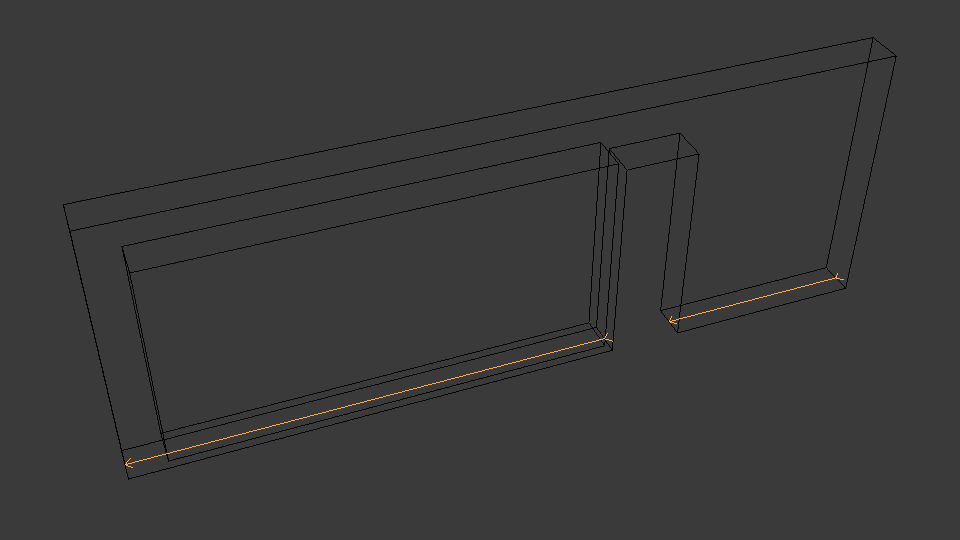
edge-arrows¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
When INCLUDE_CURVES is true and geometric elements include curves (such as the wall axis), add arrow heads to the edges to indicate direction of the curve.
IfcConvert model.ifc d4.dae --model --plan --edge-arrows -yv --include attribute GlobalId 2O2Fr$t4X7Zf8NOew3FNr2
element-hierarchy¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Warning
Only applicable to Collada .DAE output when used from IfcConvert.
Emit the relative placements from IFC instead of a flat listing of absolute placements.
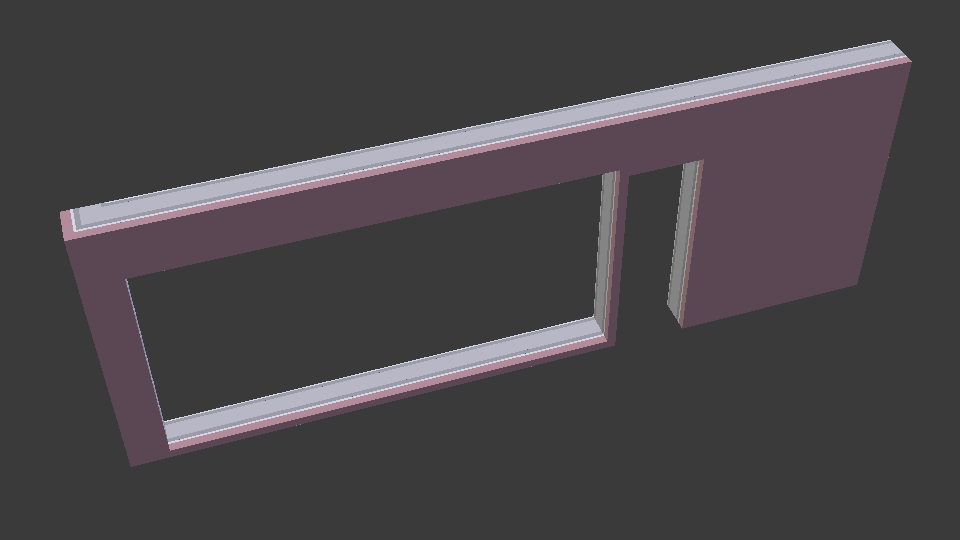
enable-layerset-slicing¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
For IfcWall and IfcSlab elements, takes the associated IfcMaterialLayerSet and builds a set of surfaces to segment the building element geometry.
Warning
Enabling this settings is computationally intensive as it involves 3D Boolean operations.
IfcConvert model.ifc d1.dae -yv --include attribute GlobalId 2O2Fr$t4X7Zf8NOew3FNr2

IfcConvert model.ifc d2.dae --enable-layerset-slicing -yv --include attribute GlobalId 2O2Fr$t4X7Zf8NOew3FNr2
force-space-transparency¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
DOUBLE |
|
0 |
Overrides transparency of spaces in geometry output.
function-step-param¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
DOUBLE |
|
0.5 |
Indicates the parameter value for defining step size when evaluating function-based curves.
function-step-type¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
INT |
|
0 |
Indicates the method used for defining step size when evaluating function-based curves. Provides interpretation of function-step-param
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
settings.set("triangulation-type", ifcopenshell.ifcopenshell_wrapper.MAXSTEPSIZE) # 0
settings.set("triangulation-type", ifcopenshell.ifcopenshell_wrapper.MINSTEPS) # 1
generate-uvs¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Applies a box projection on the generated geometry for the element to obtain UV coordinates. This is purely generated, it does not involve texture coordinates stored in the IFC model.
IfcConvert model.ifc d5.dae --generate-uvs -yv --include attribute GlobalId 2O2Fr$t4X7Zf8NOew3FNr2
iterator-output¶
By default, the iterator returns triangulated geometry. This setting allows to disable triangulation, and instead to output OpenCASCADE serialised TopoDS_Shape objects.
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
# A string representation of the OCC representation
settings.set("iterator-output", ifcopenshell.ifcopenshell_wrapper.NATIVE)
# A string representation of the OCC representation
settings.set("iterator-output", ifcopenshell.ifcopenshell_wrapper.SERIALIZED)
shape = ifcopenshell.geom.create_shape(settings, element)
print(shape.geometry.brep_data)
# CASCADE Topology V1, (c) Matra-Datavision
# Locations 0
# Curve2ds 0
# Curves 12
# 1 4.6750000000000034 -8.0749999999999904 2.657 -2.0455514041918775e-15 -1 0
# 1 4.6750000000000034 -8.0749999999999904 2.657 1 -3.435893306383461e-15 0
# 1 6.2260000000000044 -8.0749999999999957 2.657 -2.0455514041918724e-15 -1 0
# 1 6.226 -10.246000000000031 2.657 -1 6.8717866127669219e-15 0
# ...
keep-bounding-boxes¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Default is to removes IfcBoundingBox from model prior to converting geometry. Setting this option disables that behaviour.
layerset-first¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
When not using APPLY_LAYERSETS, take the first material layer from the set to use as the material for the overall element.
length-unit¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
DOUBLE |
|
1 |
Override the length unit being defined in the IFC as a factor of meters.
mesher-angular-deflection¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
DOUBLE |
|
0.5 |
Sets the angular tolerance of the mesher in radians.
Here is an example in C++:
SerializerSettings settings;
double tolerance;
// ...
settings.set_angular_tolerance(tolerance);
Here is an example in Python:
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
settings.set("mesher-angular-deflection", 0.5)
mesher-linear-deflection¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
DOUBLE |
|
1e-3 |
Sets the deflection tolerance of the mesher.
Here is an example in C++:
SerializerSettings settings;
double tolerance;
// ...
settings.set_deflection_tolerance(tolerance);
Here is an example in Python:
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
settings.set("mesher-linear-deflection", 1e-3)
model-offset¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
ARRAY<DOUBLE> |
|
0,0,0 |
Sets an offset to be applied to all the matrixes of geometries returned from the iterator.
In Python, this is set in the settings passed to the iterator.
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
settings.set("model-offset", (1.0, 2.0, 3.0))
model-rotation¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
ARRAY<DOUBLE> |
|
0,0,0,0 |
Applies an arbitrary quaternion rotation of form ‘x,y,z,w’ to all placements.
no-normals¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Do not emit normals on geometric output. Saves time and filesize.
no-parallel-mapping¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Perform mapping upfront (single-threaded) as opposed to in parallel. May decrease performance, but also decrease output size (in the future)
no-wire-intersection-check¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Disables wire intersection checks. These checks are done on faces to prevent self-intersections of face bounds. Self-intersections reduce the reliability of boolean operations and may lead to crashes.
no-wire-intersection-tolerance¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Set wire intersection tolerance to 0. By default the above check is done using a tolerance criterium. So that when a vertex is a certain epsilon distance away from an edge this is flagged as an intersection.
precision¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
DOUBLE |
|
0 |
By default the precision specified by the IFC model is used. You may set this to a custom precision.
precision-factor¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
DOUBLE |
|
0 |
Option to increase linear tolerance for more permissive edge curves and fewer artifacts after boolean operations at the expense of geometric detail due to vertex collapsing and wire intersection fuzziness. This is multiplied to the precision.
reorient-shells¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Re-orient or sew connected face sets to have a consistent outwards orientation.
site-local-placement¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
See building-local-placement, but exclude also the ObjectPlacement of the IfcSite.
surface-colour¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Prioritizes the surface color instead of using diffuse.
triangulation-type¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
INT |
|
0 |
Type of planar facet to be emitted.
settings = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
settings.set("triangulation-type", ifcopenshell.ifcopenshell_wrapper.TRIANGLE_MESH) # 0
settings.set("triangulation-type", ifcopenshell.ifcopenshell_wrapper.POLYHEDRON_WITHOUT_HOLES) # 1
settings.set("triangulation-type", ifcopenshell.ifcopenshell_wrapper.POLYHEDRON_WITH_HOLES) # 2
unify-shapes¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Unify adjacent co-planar and co-linear subshapes (topological entities sharing the same geometric domain) before triangulation or further processing
use-material-names¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Use material names instead of unique IDs for naming materials upon serialization. Applicable for OBJ and DAE output.
use-python-opencascade¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
N/A |
False |
Warning
Only available in Python when an import of OCC.Core.BRepTools or OCC.BRepTools succeeds.
This implies use-world-coords and iterator-output set to SERIALIZED.
The serialized TopoDS_Shape from iterator output is deserialized by Python OpenCASCADE.
use-world-coords¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Apply the ObjectPlacement of the building elements to the geometric output. This is implied when using the Wavefront .OBJ output in IfcConvert. Note that this also eliminates the possibility for geometric elements to point to the same interpreted geometry result.
validate¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False |
Running IfcConvert with --validate will set a non-zero exit code when ever a log message with severity equal or greater than ERROR has been emitted.
Currently for internal use only. For every building element geometry converted, looks for an associated quantity set where the OwnerHistory’s organization name is IfcOpenShell. And looks for the quantities “Total Surface Area”, “Volume”, “Shape Validation Properties.Surface Genus” and validates these according to the interpreted geometry definition. Emit Logger::Error when calculated values are outside of the tolerance range for the value stored in the model.
weld-vertices¶
Type |
IfcConvert Option |
Default |
|---|---|---|
BOOL |
|
False in IfcConvert, True in C++ and Python |
Note
This setting only affects triangulated output.
Discards normals and joins vertices solely based on position. This is useful when output is to be modified in a modeling application.
>>> import ifcopenshell, ifcopenshell.geom
>>> s = ifcopenshell.geom.settings()
>>> s.set(s.WELD_VERTICES, False)
>>> f = ifcopenshell.open("model.ifc")
>>> c = f["3bXiCStxP6Fgxdej$yc50U"]
>>> shp = ifcopenshell.geom.create_shape(s, c)
>>> shp.geometry.verts
(4.675000000000003, -8.07499999999999, 2.657, 4.674999999999999, -10.24600000000002, 2.657, 6.226000000000004, -8.074999999999996, 2.657, 6.226, -10.24600000000003, 2.657, 4.675000000000003, -8.07499999999999, 2.6, 4.674999999999999, -10.24600000000002, 2.6, 6.226000000000004, -8.074999999999996, 2.6, 6.226, -10.24600000000003, 2.6, 4.674999999999999, -10.24600000000002, 2.657, 4.674999999999999, -10.24600000000002, 2.6, 4.675000000000003, -8.07499999999999, 2.657, 4.675000000000003, -8.07499999999999, 2.6, 6.226, -10.24600000000003, 2.657, 4.674999999999999, -10.24600000000002, 2.657, 6.226, -10.24600000000003, 2.6, 4.674999999999999, -10.24600000000002, 2.6, 6.226000000000004, -8.074999999999996, 2.657, 6.226, -10.24600000000003, 2.657, 6.226000000000004, -8.074999999999996, 2.6, 6.226, -10.24600000000003, 2.6, 4.675000000000003, -8.07499999999999, 2.657, 4.675000000000003, -8.07499999999999, 2.6, 6.226000000000004, -8.074999999999996, 2.657, 6.226000000000004, -8.074999999999996, 2.6)
>>> shp.geometry.normals
(3.059754518198021e-17, 0.0, -1.0, 3.059754518198021e-17, 0.0, -1.0, 3.059754518198021e-17, 0.0, -1.0, 3.059754518198021e-17, 0.0, -1.0, 2.110175529791737e-16, 0.0, -1.0, 2.110175529791737e-16, 0.0, -1.0, 2.110175529791737e-16, 0.0, -1.0, 2.110175529791737e-16, 0.0, -1.0, -1.0, 1.79434333701042e-15, 0.0, -1.0, 1.79434333701042e-15, 0.0, -1.0, 1.79434333701042e-15, 0.0, -1.0, 1.79434333701042e-15, 0.0, 6.8717866127669046e-15, 1.0, 0.0, 6.8717866127669046e-15, 1.0, 0.0, 6.8717866127669046e-15, 1.0, 0.0, 6.8717866127669046e-15, 1.0, 0.0, -1.0, 1.79434333701042e-15, 0.0, -1.0, 1.79434333701042e-15, 0.0, -1.0, 1.79434333701042e-15, 0.0, -1.0, 1.79434333701042e-15, 0.0, 3.4358933063834523e-15, 1.0, 0.0, 3.4358933063834523e-15, 1.0, 0.0, 3.4358933063834523e-15, 1.0, 0.0, 3.4358933063834523e-15, 1.0, 0.0)
>>>
>>> s.set(s.WELD_VERTICES, True)
>>> shp = ifcopenshell.geom.create_shape(s, c)
>>> shp.geometry.verts
(4.675000000000003, -8.07499999999999, 2.657, 4.674999999999999, -10.24600000000002, 2.657, 6.226000000000004, -8.074999999999996, 2.657, 6.226, -10.24600000000003, 2.657, 4.675000000000003, -8.07499999999999, 2.6, 4.674999999999999, -10.24600000000002, 2.6, 6.226000000000004, -8.074999999999996, 2.6, 6.226, -10.24600000000003, 2.6)
>>> shp.geometry.normals
()